Location: Tischlerei Eigenstetter
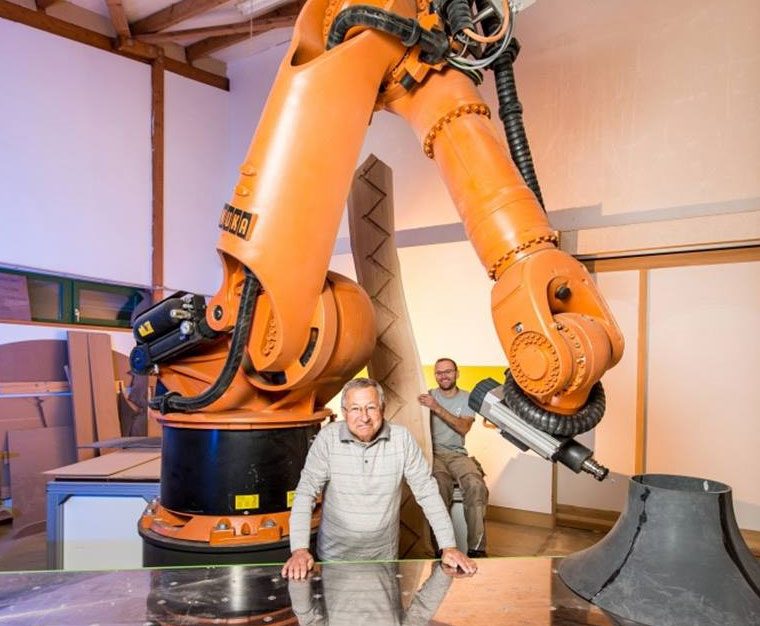
FORTEC is not quite as huge in reality, but it is certainly the heavyweight among the robots in the research project.
Location: Tischlerei Eigenstetter
Location: werk5 new craft, Strehl Kinderrehatechnik
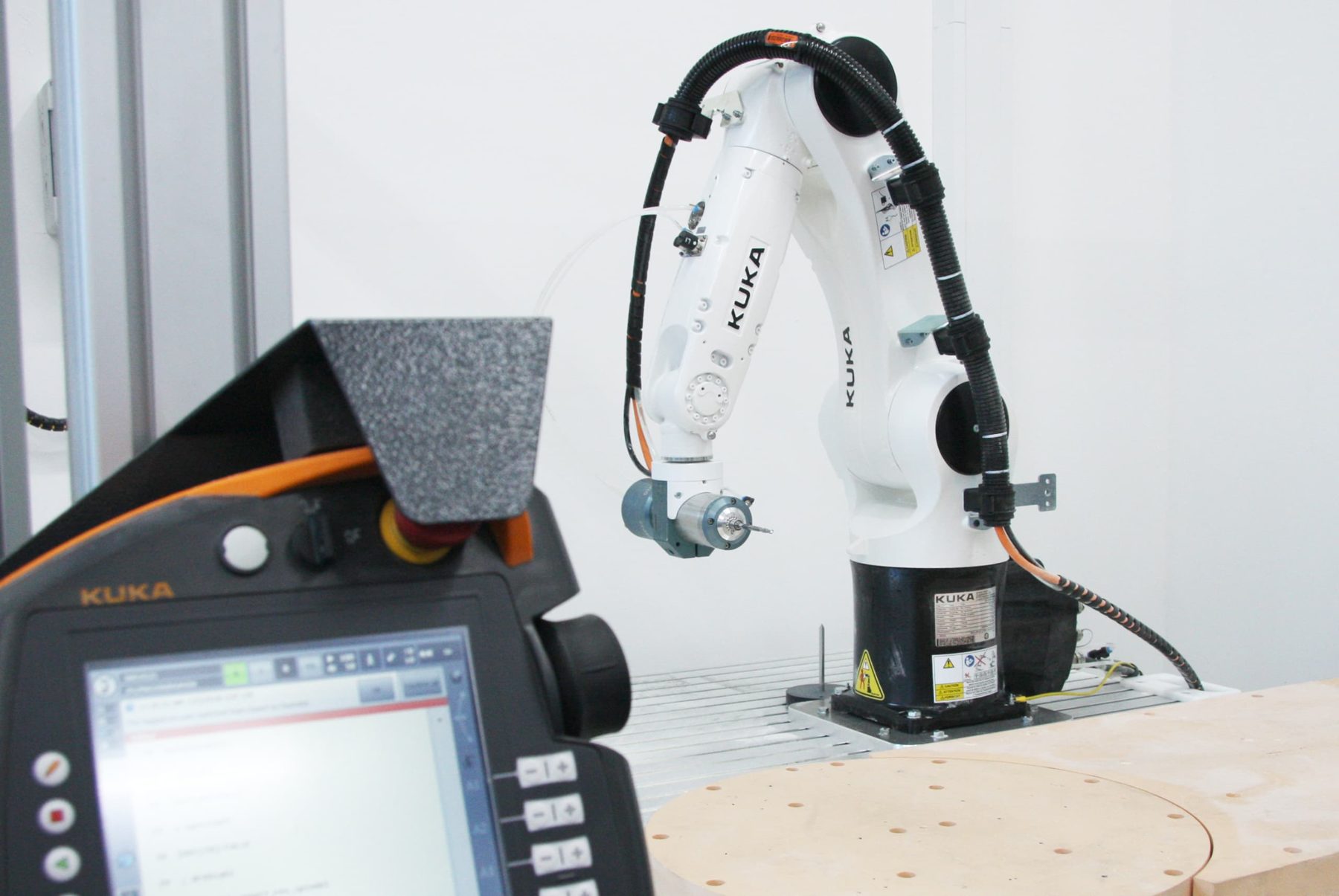
6-axis industrial robot with synchronized turntable
Location: werk5 new craft
A LEROSH test candidate: iisy – One of the 3 new cobots from KUKA’s iisy series
A development of the Institute of Robotics and Mechatronics at DLR ( > SARA )
More sensitive and more range than comparable cobots.
Where does the SARA show its advantages?
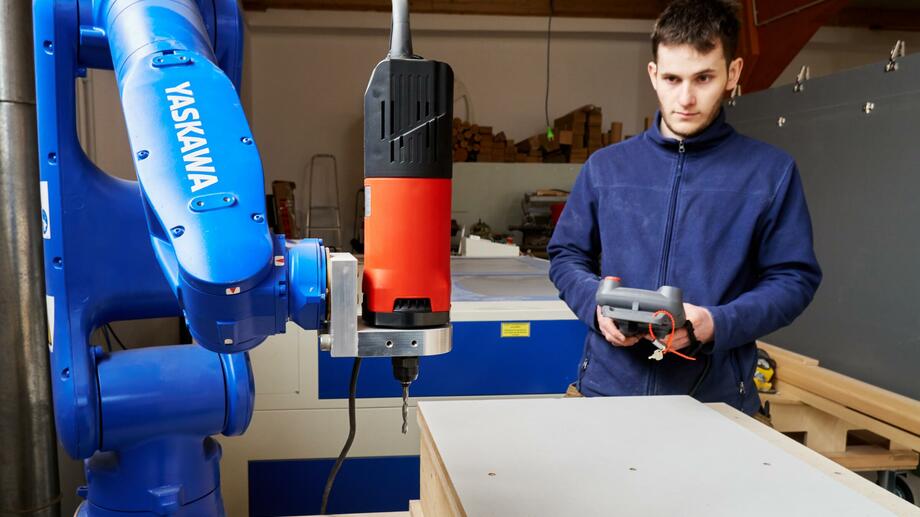
Location: Tischlerei Eigenstetter
Location: Tischlerei Eigenstetter
Robots