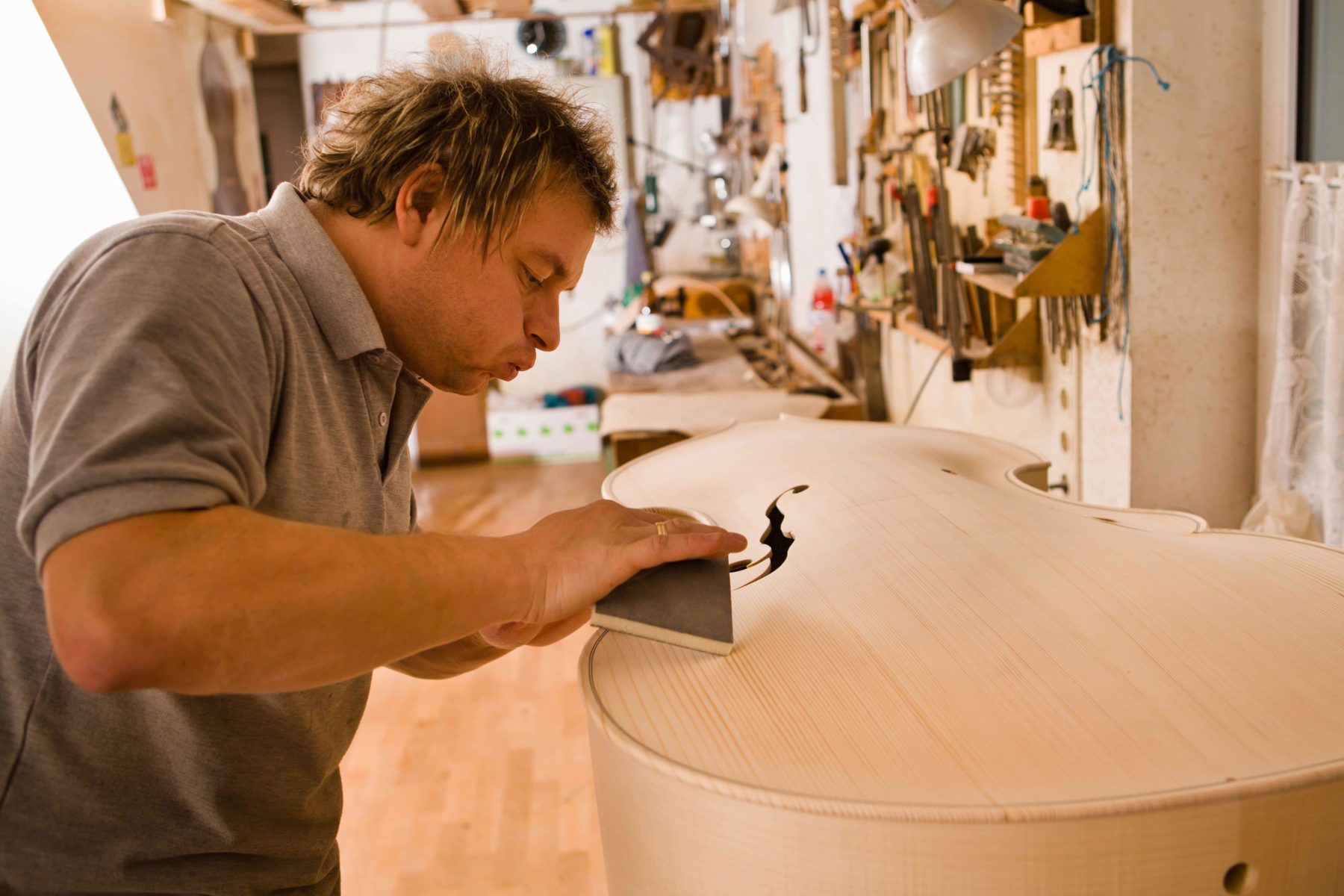
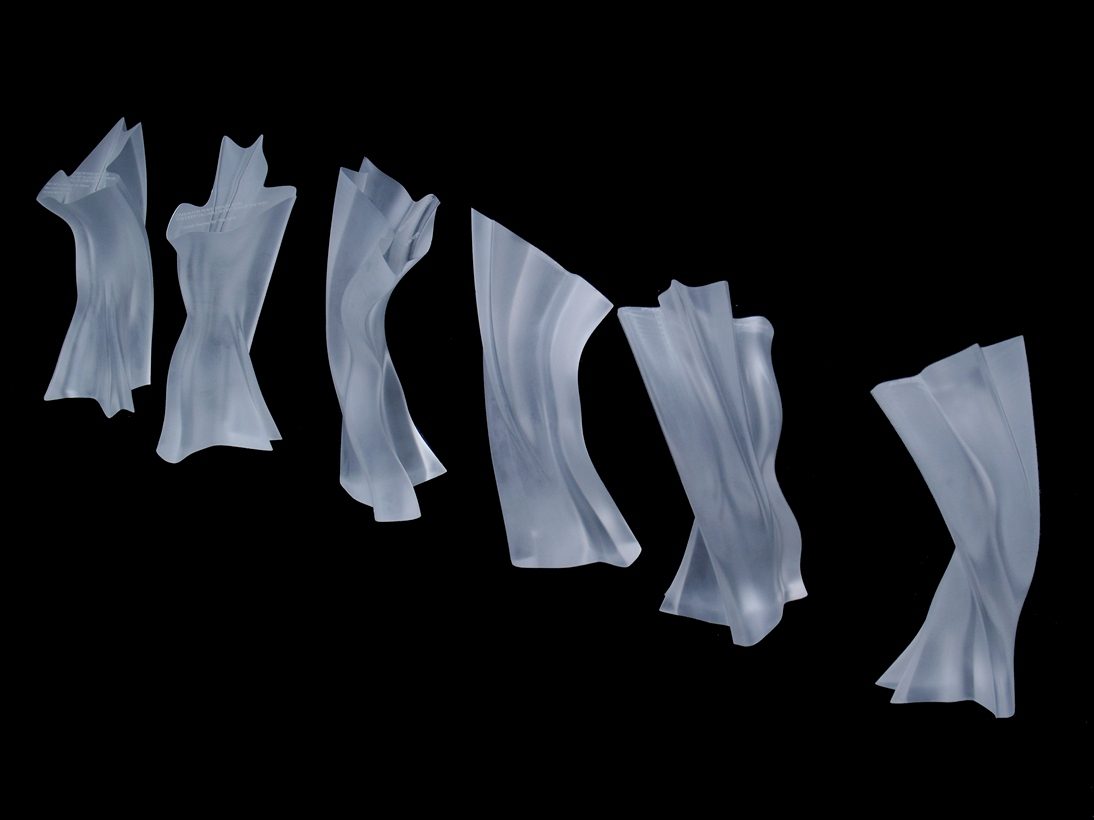
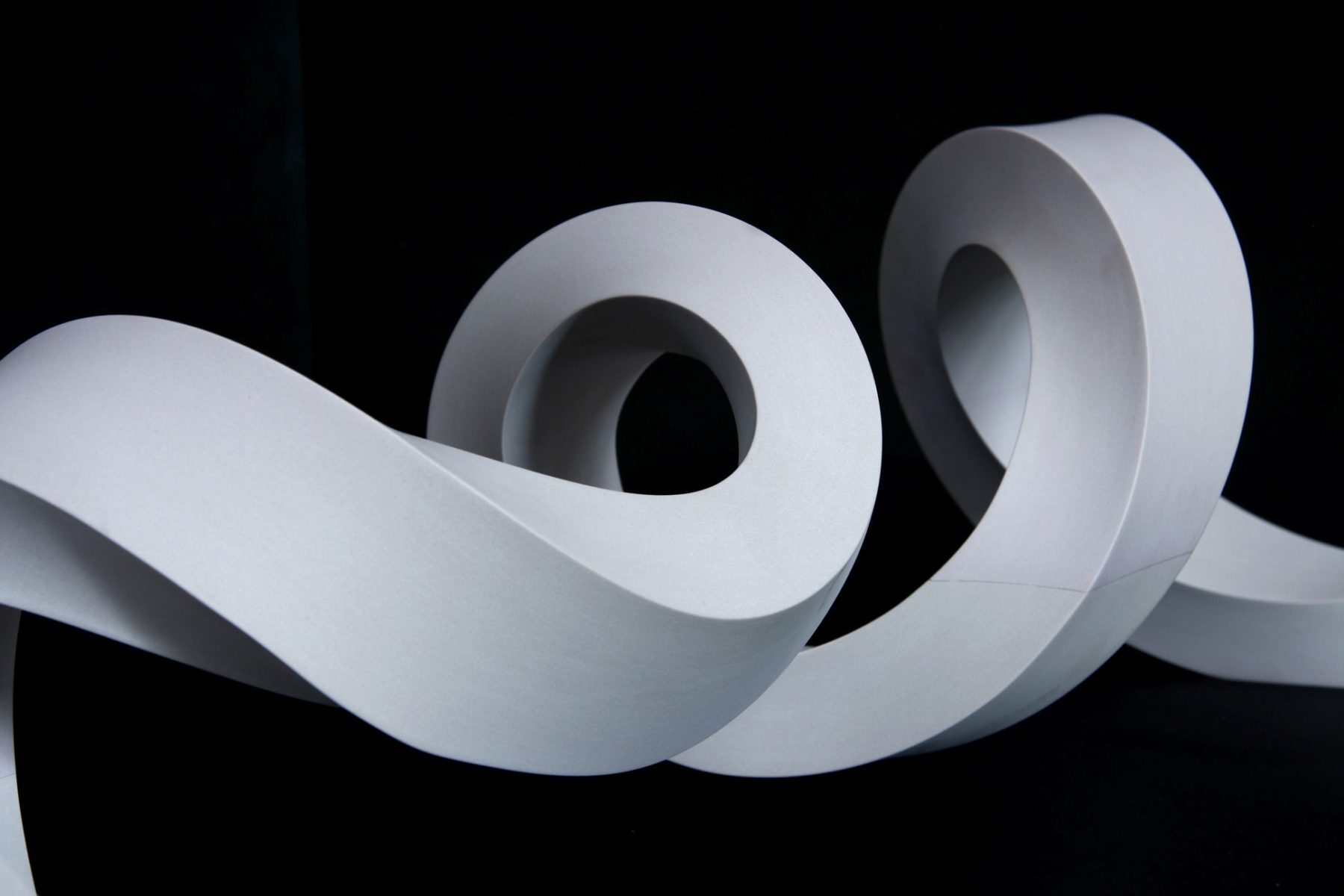
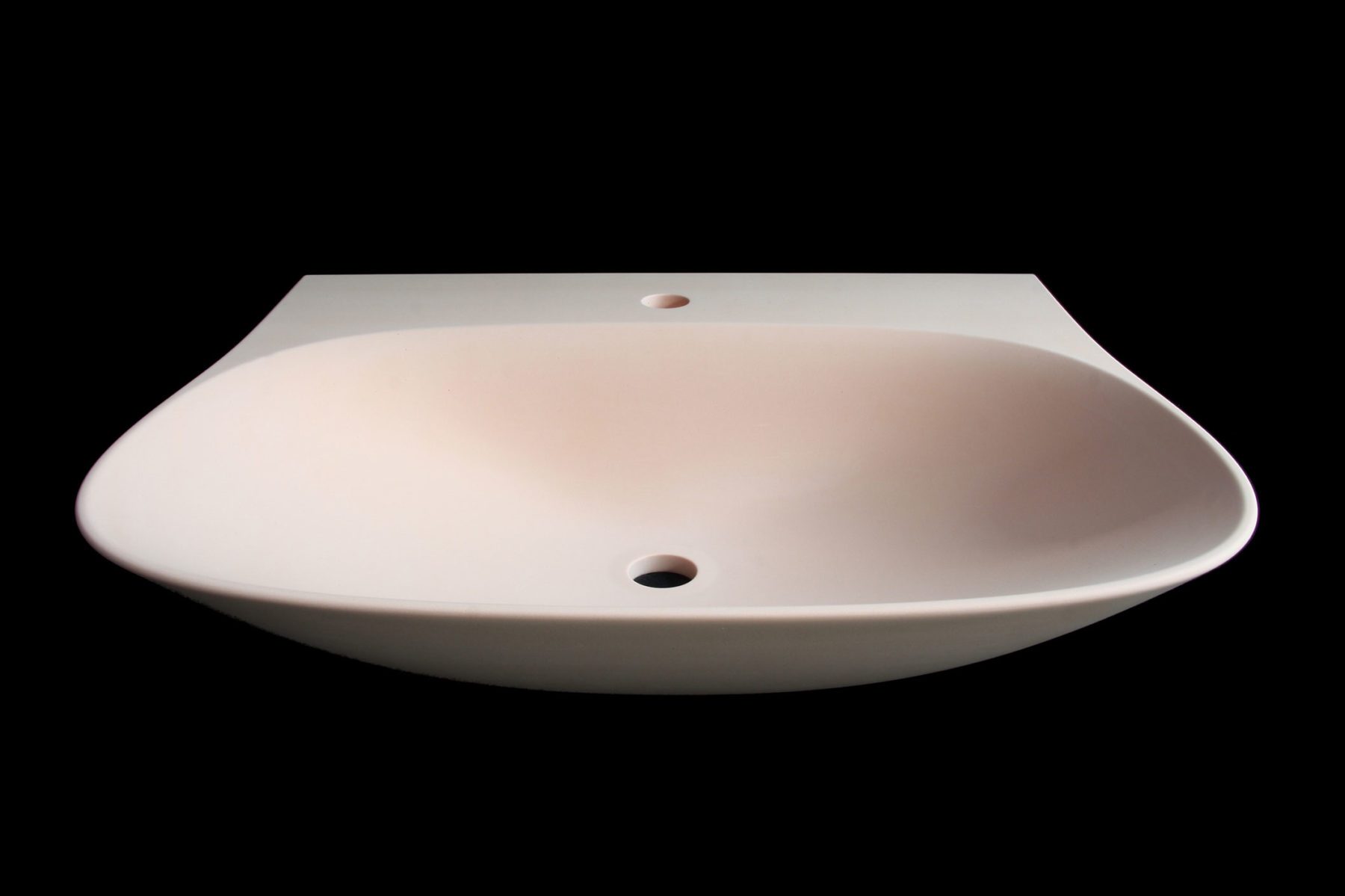
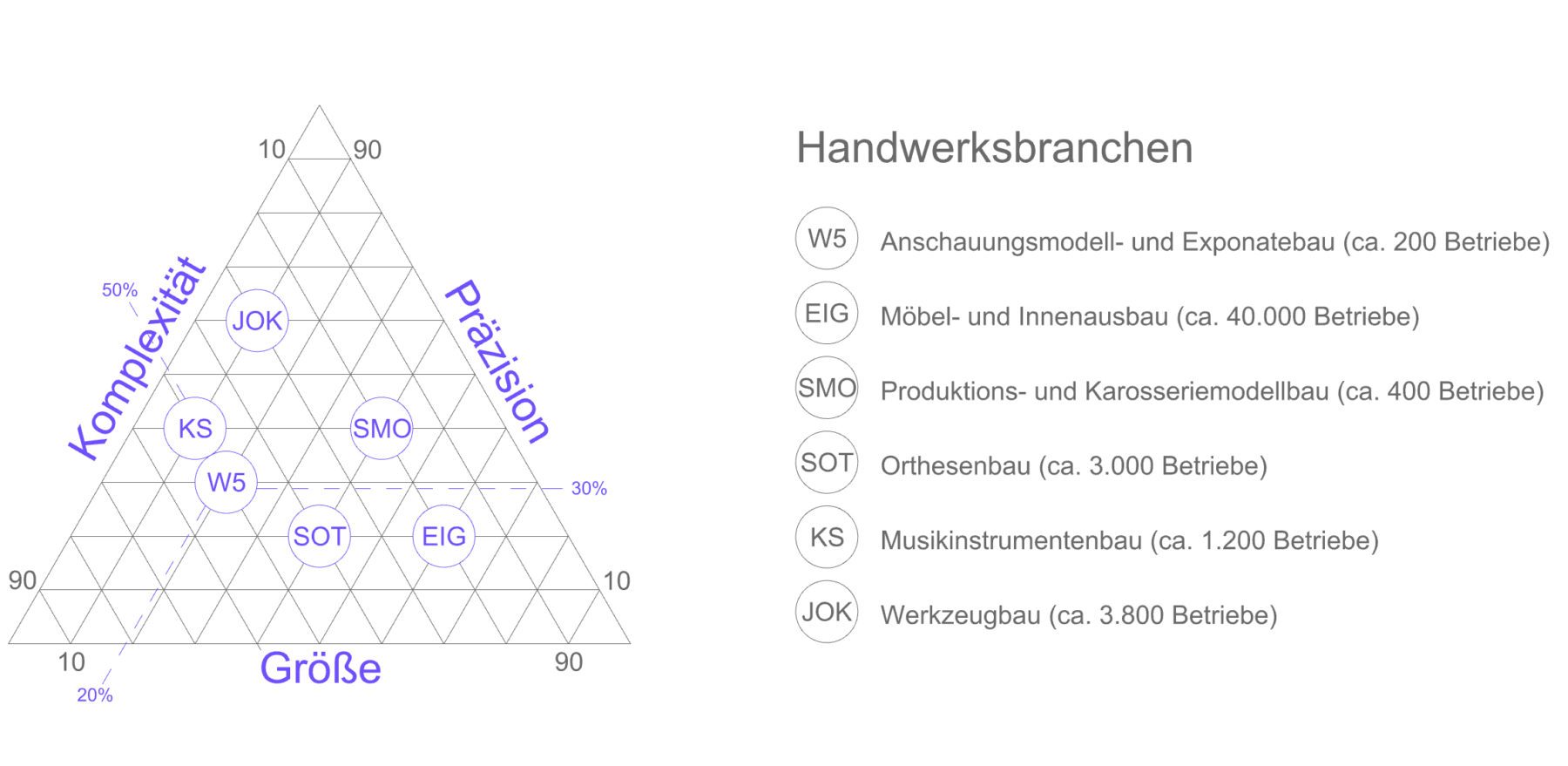
This wide range of materials is to be processed at the participating craft companies:
Solid spruce wood for cello lids, molded wood materials for spiral staircases, composite materials or aluminum for vehicle parts, carbon offcuts for orthotic construction, and a wide variety of plastics for 3D shaping in the field of design and art.
How is the experience of craftsmanship in handling a wide variety of materials transferred to a sensory and learning system?
For example, can the vibration of a wooden panel be evaluated and used to control the grinding process?
Styrofoam 15 kg/m³
Foam 35 kg/m³
PU rigid foam 80-1,200 kg/m³
Spruce wood 500 kg/m³
MDF 600kg/m³
Oak wood 800 kg/m³
Acrylic 1.200kg/m²
Ebony 1.300 kg/m³
Carbon fiber materials (CFK) 1.600 kg/m³
Solid surface material 1,700 kg/m³
Glass fiber materials (CFK) 2,500 kg/m³
Aluminum (Al) 2,700 kg/m³
Iron (Fe) 7,900 kg/m³
Material